LLM知识蒸馏代码讲解及训练实验
知识蒸馏简单讲即使用大规模参数的模型对小规模参数模型进行蒸馏,且不是简单的只使用答案,是需要两个模型的log prob进行交互的,故两个模型的vocab size必须是一样的。参考论文中分类了多个不同的版本,on-policy及off-policy。
LLM知识蒸馏代码讲解及训练实验
知识蒸馏简单讲即使用大规模参数的模型对小规模参数模型进行蒸馏,且不是简单的只使用答案,是需要两个模型的log prob进行交互的,故两个模型的vocab size必须是一样的。
参考论文中分类了多个不同的版本,on-policy及off-policy。
TRL GKD
代码基于trl实现的GKDTrainer,GKDTrainer继承自SFTTrainer,SFTTrainer继承自Trainer。所以下面我们先简单的介绍一下Trainer和SFTTrainer
Trainer
正常的我们使用Trainer训练,是要把数据拼接成一段文本,我们需要自己手动进行处理。
例如prompt output的数据格式,将其拼接,然后通过label来决定学习的部分,
通常情况下只学习output中的。所以一般给的数据就是三个字段的dataset字典形式:["input_ids", "labels", "attention_mask"]
SFTTrainer
SFTTrainer继承自Trainer,进行了一些简单的包装。主要还是在数据层面,这其中就包括下面这个函数,对数据进行判断然后再返回、再自动拼接等。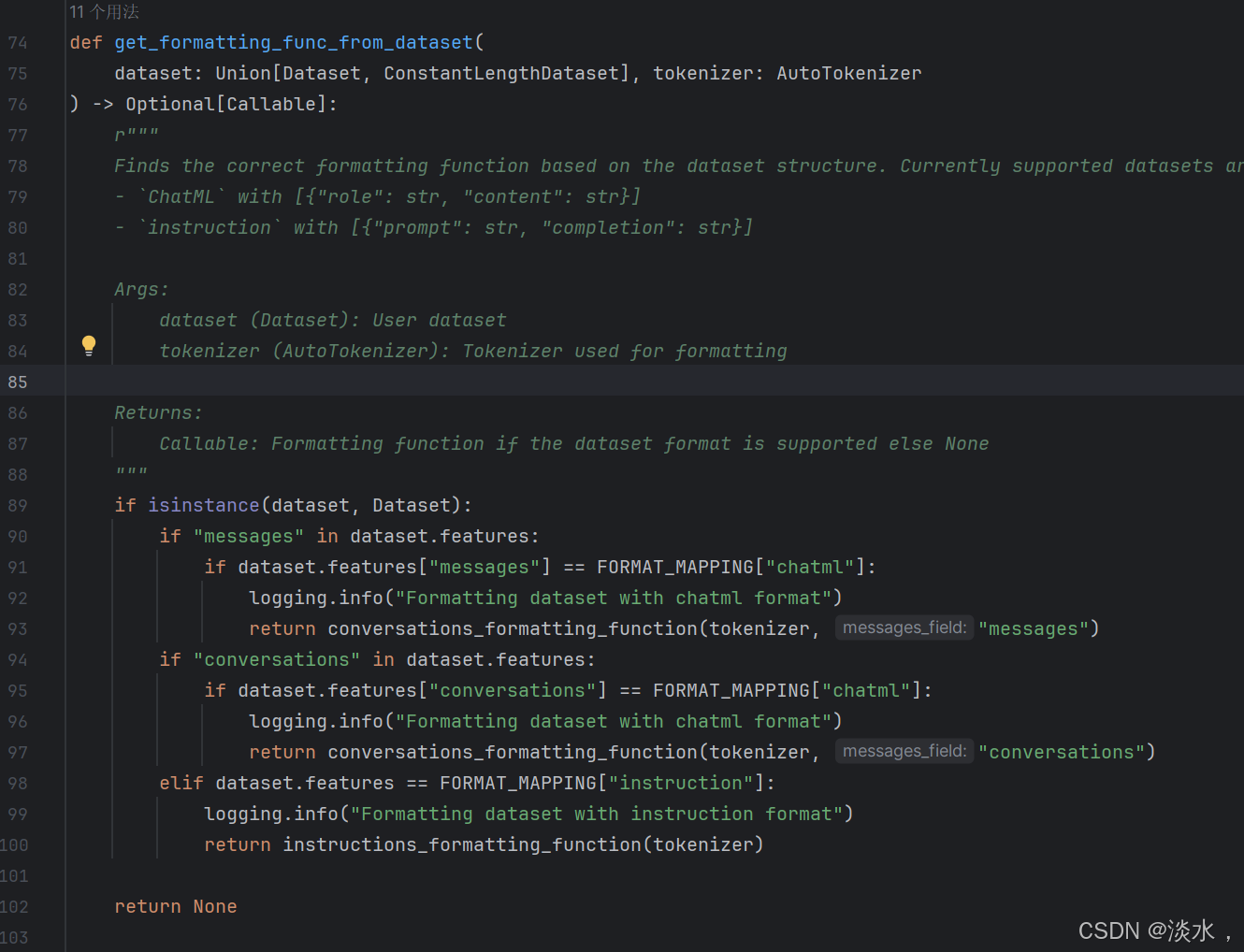
最终其返回的数据还是跟Trianer中需要输入的dataset形式一样,包含SFT数据的["input_ids", "labels", "attention_mask"]三个字段。
不过输入的数据格式就有了明确的要求,需要包含一个“message”的列表(最好也包含一个prompt字段,不过没有也没关系,会自动根据message中的user作为prompt,具体实现是在GKDTrainer中调用utils的DataCollatorForChatML函数实现的),其中一般包括字典,字段的字段为:
- role:system,assistant ,user
- content: 内容
即常规的template格式,示例如下:
{"messages":[{"role":"user","content":"show me the swift adaptation of this:\ndef fibfib_with_offset(n: int, offset: int):\n fibfib = [1] * (n + offset + 1)\n\n for i in range(max(offset, 2), n + offset + 1):\n fibfib[i] = fibfib[fibfib[i-1]] + fibfib[fibfib[i-2]]\n\n return fibfib[n + offset]\n\n# Test the function\nprint(fibfib_with_offset(5, 2)) # Output: 3"},{"role":"assistant","content":"Here is the Swift adaptation of your Python code:\n\n```swift\nfunc fibfib_with_offset(n: Int, offset: Int) -> Int {\n var fibfib = [Int](repeating: 1, count: n + offset + 1)\n\n for i in max(offset, 2)...(n + offset) {\n fibfib[i] = fibfib[fibfib[i-1]] + fibfib[fibfib[i-2]]\n }\n\n return fibfib[n + offset]\n}\n\n\/\/ Test the function\nprint(fibfib_with_offset(n: 5, offset: 2)) \/\/ Output: 3\n```\n\nPlease note that Swift uses closed range operator (`...`) in loops to include both endpoints of the range, similar to Python's `range()` function. Also, array indexing and length calculation in Swift are similar to Python. That's why I used the same approach to define the length of the `fibfib` array and to read and write to its elements."}]}
GKDTrainer
知识蒸馏分很多种,而GKD则是其中的一种。论文中对比了几种相关的训练方式:
- Supervised KD
- SFT
- SeqKD
- GKD
以数据
{instruct:今天天气如何?output:很好!}
为例
对比一下上述三种训练方式的不同:
1、SFT就不用解释了,一种非常常规的方式。
2、Supervised KD是指使用训练数据的output作为答案,将数据拼接后 今天天气如何?很好!,这作为一条数据输入给模型,维度为[1,8,35206],分别表示为batch、seq_len、vocab_size(这里我们假设模型的vocab size为35206)。
student模型和teacher模型接收这条输入后,经过模型层,输出维度相同的logsits,故维度仍为[1,8,35206]。然后将student和teacher的输出做loss。loss有很多可以选择,论文中采用的是Jensen-Shannon Divergence loss,JSD我们下面会介绍。
3、SeqKD 是指仅输入模型的prompt,使用teacher模型生成output后,然后再重复2中的内容,拼接数据后分别给teacher和student,输出相同维度的logits并进行loss计算。论文原话: trains on output sequences generated by the teacher.can be viewed as supervised FT on teacher-generated outputs.
4、GKD:使用student模型生成output,这就属于on policy的方式了,模型每次更新权重后都会进行output输出,再反馈到训练中。
总的来说,前三者基本都属于off-policy,最后的GKD属于on-policy。
GKDTrainer 使用及详解
知识蒸馏与SFT主要的不同是在于计算loss阶段,常规的SFT计算loss我们已经很熟悉了,即logits与label计算交叉熵。而知识蒸馏的loss则是student模型与teacher模型的 logits进行散度计算,常用的就是Jensen-Shannon Divergence (JSD)和KLD。要了解JSD首先需要了解一下KLD
KL散度
KL散度比较常规,公式如下: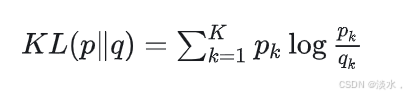
首先我们来看一下如何计算KL。可以自己算也可以使用pytorch的kl_div函数,示例如下:
要明确的一点是公式这里的P、Q为经过softmax后的输出结果,并没有经过log,这一点非常重要,因为后面会有相关问题。
test1是自己根据公式的计算方式,test2使用torch的kl_div函数进行计算,其中reduction表示是否求和、求平均等选项,log_target表示是否对target(也就是P)进行log运算,默认就是False。
import torch
import torch.nn.functional as F
P = torch.Tensor([0.36, 0.48, 0.16])
Q = torch.Tensor([0.333, 0.333, 0.333])
test1 = (P * (P / Q).log())
# tensor([ 0.0281, 0.1755, -0.1173])
test2 = F.kl_div(Q.log(), P, reduction="none", log_target=False)
# tensor([ 0.0281, 0.1755, -0.1173])
可以看到最终的计算结果是一样的。
JS散度
由于KL散度是不对称的,在知识蒸馏中使用JSD,Jensen-Shannon Divergence 是基于KL散度改进的更平滑和对称的概率分布度量。论文中给出了其改进的计算公式: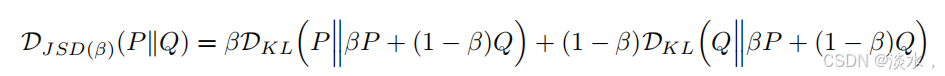
trl中也已经实现了其计算代码:
def generalized_jsd_loss(
student_logits, teacher_logits, labels=None, beta=0.5, temperature=1.0, reduction="batchmean"
):
# Apply temperature scaling
student_logits = student_logits / temperature
teacher_logits = teacher_logits / temperature
# Compute log probabilities for student and probabilities for teacher
student_log_probs = F.log_softmax(student_logits, dim=-1)
teacher_log_probs = F.log_softmax(teacher_logits, dim=-1)
# Compute the log of the mixture distribution
# log(a + b) = log(exp(log(a)) + exp(log(b))) -> for mixture
beta = torch.tensor(beta, dtype=student_log_probs.dtype)
mixture_log_probs = torch.logsumexp(
torch.stack([student_log_probs + torch.log(beta), teacher_log_probs + torch.log(1 - beta)]),
dim=0,
)
# Compute KL divergences using F.kl_div
# PyTorch differs from the standard mathematical definition, so the order of the probability distributions is swapped compared to that defined in the paper.
kl_teacher = F.kl_div(mixture_log_probs, teacher_log_probs, reduction="none", log_target=True)
kl_student = F.kl_div(mixture_log_probs, student_log_probs, reduction="none", log_target=True)
# Compute the Generalized Jensen-Shannon Divergence
jsd = beta * kl_teacher + (1 - beta) * kl_student
# Masking
if labels is not None:
mask = labels != -100
jsd = jsd[mask]
# Apply reduction
if reduction == "batchmean":
return jsd.sum() / mask.sum() if labels is not None else jsd.sum() / (jsd.size(0) * jsd.size(1))
elif reduction == "sum":
return jsd.sum()
elif reduction == "mean":
return jsd.mean()
else:
return jsd
其计算KL是采用的torch的F.kl_div函数,
kl_teacher = F.kl_div(mixture_log_probs, teacher_log_probs, reduction="none", log_target=True)
正常计算KL时传入的第一个参数应该做log计算,而第二个参数不做log计算,但是我们的student_log_probs和 teacher_log_probs分别是经过log softmax后的张量,故正如上面KL章节所提到的,在这里需要将log_target设置为True,这样其Target相当于是两次log计算,也就是相当于没有log计算。
Quick Start
知识蒸馏训练已经集成至github:
https://github.com/mst272/LLM-Dojo/blob/main/rlhf/README.md#knowledge-distillation
知识蒸馏训练的启动方式也非常简单,可以一键式启用,只是需要注意几个控制参数即可:
- lmbda:0时为Supervised KD,1时为GKD。可在[0,1]范围内选择,这样就会混合比例
- beta: 0时loss为KLD, 1时为JSD。可在[0,1]范围内选择,这样就会混合比例
- seq_kd: True时Supervised KD将替换为Seq KD,默认为False,其他不变。(最近才合并的PR,trl还没有更新,暂时先写下)
启动脚本如下,支持deepspeed训练。
# Lora模式, 如需QLora或者全参略微修改参数即可
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=2,3 accelerate launch --ds_config ./dszero3.yaml ../gkd.py \
--model_name_or_path deepseek-coder-6.7b-instruct \
--teacher_model_name_or_path deepseek-coder-33b-instruct\
--dataset_name ../data_example/gkd_data.jsonl \
--learning_rate 2e-5 \
--per_device_train_batch_size 4 \
--gradient_accumulation_steps 8 \
--output_dir gkd-model2 \
--logging_steps 2 \
--num_train_epochs 1 \
--gradient_checkpointing \
--lmbda 0.5 \
--beta 0.5 \
--use_peft \
--lora_r 32 \
--lora_alpha 16 \
--trust_remote_code \
--bf16 \
--save_strategy "steps" \
--save_steps 180 \
--save_total_limit 5 \
--warmup_steps 10 \
--lr_scheduler_type "cosine" \
--torch_dtype bfloat16 > logs.log 2>&1 &
以deepseek为例进行实验
使用deepseek 7b作为student model,deepseek 33b作为teacher model进行训练,
lmbda与beta均设置为0.5,也就是混合方法。进行代码大模型相关的训练,参考指标为Humaneval。
通过实验可观察到student模型训练后的好坏强依赖teacher模型。
首先直接进行知识蒸馏,效果不是很理想,考虑到可能的原因是是teacher model能力并没有太强。
故在数据集上对teacher model进行SFT,然后使用相同数据进行知识蒸馏,结果显示Student模型的到了明显的提升。
参考:
1、https://huggingface.co/papers/2306.13649
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献1条内容
已为社区贡献1条内容







所有评论(0)