故事翻译及自动标注重点单词功能、四六级真题功能、每日阅读功能的开发与实现及部分前端页面的优化 ---第十三周+十四周+十五周
构建历史消息列表,通过 uiState.fullResponse.split("\n\n\n") 将完整的对话历史分割成多个部分,并从中提取出用户的输入和助手的回答,然后使用 chunked(2) 将每一轮对话(用户输入和助手回答)配对成一个 Pair。当前考试集管理,使用 StateFlow 管理当前显示的考试集索引,对外暴露为不可变的 StateFlow。进行整篇文章的阅读,点击单词显示其释义
一、故事翻译及自动标注重点单词功能
1.我们项目的互动式情景、中英文翻译及解析功能需要与DeepSeek连续对话。我们团队通过对消息列表的构建维护DeepSeek的历史上下文,实现连续对话和重新回答功能,完整代码实现如下:
fun streamResponse(messages: List<Pair<String, String>>, prompt: String): Flow<String> = callbackFlow {
val url = "$apiBase/chat/completions"
val jsonMessages = JSONArray().apply {
for ((userInput, assistantReply) in messages) {
put(JSONObject().apply {
put("role", "user")
put("content", userInput)
})
put(JSONObject().apply {
put("role", "assistant")
put("content", assistantReply)
})
}
put(JSONObject().apply {
put("role", "user")
put("content", prompt)
})
}
val payload = JSONObject().apply {
put("model", model)
put("messages", jsonMessages)
put("temperature", 0.7)
put("max_tokens", 1024)
put("stream", true)
}
val request = withContext(Dispatchers.IO) {
Request.Builder()
.url(url)
.header("Authorization", "Bearer $apiKey")
.header("Content-Type", "application/json")
.post(payload.toString().toRequestBody())
.build()
}
val eventSourceFactory = EventSources.createFactory(client)
val finalResponse = StringBuilder()
val eventSourceListener = object : EventSourceListener() {
override fun onEvent(
eventSource: EventSource,
id: String?,
type: String?,
data: String
) {
val trimmedData = data.trim()
Log.d("DeepSeekDebug", "收到完整数据: $trimmedData")
if (trimmedData == "[DONE]") {
// 请求结束时打印最终结果
Log.d("DeepSeekDebug", "请求完成,最终回复: $finalResponse")
close()
return
}
try {
val jsonObject = JSONObject(trimmedData)
val choices = jsonObject.getJSONArray("choices")
if (choices.length() > 0) {
val delta = choices.getJSONObject(0).getJSONObject("delta")
if (delta.has("content")) {
val content = delta.getString("content")
finalResponse.append(content)
trySend(content)
}
}
} catch (e: Exception) {
trySend("\n[解析错误] ${e.message}")
}
}
override fun onFailure(
eventSource: EventSource,
t: Throwable?,
response: Response?
) {
trySend("\n[API请求错误] ${t?.message}")
close(t)
}
override fun onClosed(eventSource: EventSource) {
close()
}
}
val eventSource = eventSourceFactory.newEventSource(request, eventSourceListener)
awaitClose {
eventSource.cancel()
}
}2.消息列表的构建与持久化
构建历史消息列表,通过 uiState.fullResponse.split("\n\n\n") 将完整的对话历史分割成多个部分,并从中提取出用户的输入和助手的回答,然后使用 chunked(2) 将每一轮对话(用户输入和助手回答)配对成一个 Pair。
val history = uiState.fullResponse.split("\n\n\n").mapNotNull {
val parts = it.split(": ", limit = 2)
if (parts.size == 2) parts[1] else null
}.chunked(2).map {
it[0] to (it.getOrNull(1) ?: "")
}然后将该列表传递给 deepSeekService.streamResponse 方法:
deepSeekService.streamResponse(history, prompt)3.临时对话存储 ,使用单例模式来容纳一个线程安全的静态变量,并对其进行控制,避免受到 ViewModel 生命周期的影响,这里使用_globalContent维护全局历史消息,使用Mutex确保线程安全。
private const val TAG = "GlobalTracker"
private var _globalContent: String = ""
private val mutex = Mutex()
val globalContent: String
get() = _globalContent
suspend fun appendContent(newContent: String) {
mutex.withLock {
_globalContent += newContent
Log.d(TAG, "globalContent 发生变化: $_globalContent")
}
}4.对话消息持久化,定义对话历史实体类:
@Entity(tableName = "chat_history")
data class ChatHistoryEntity(
@PrimaryKey(autoGenerate = true) val id: Int = 0, // 消息ID
val timestamp: Long = System.currentTimeMillis(), // 时间戳
val role: String, // 角色
val content: String // 内容
)5.实现界面如下:
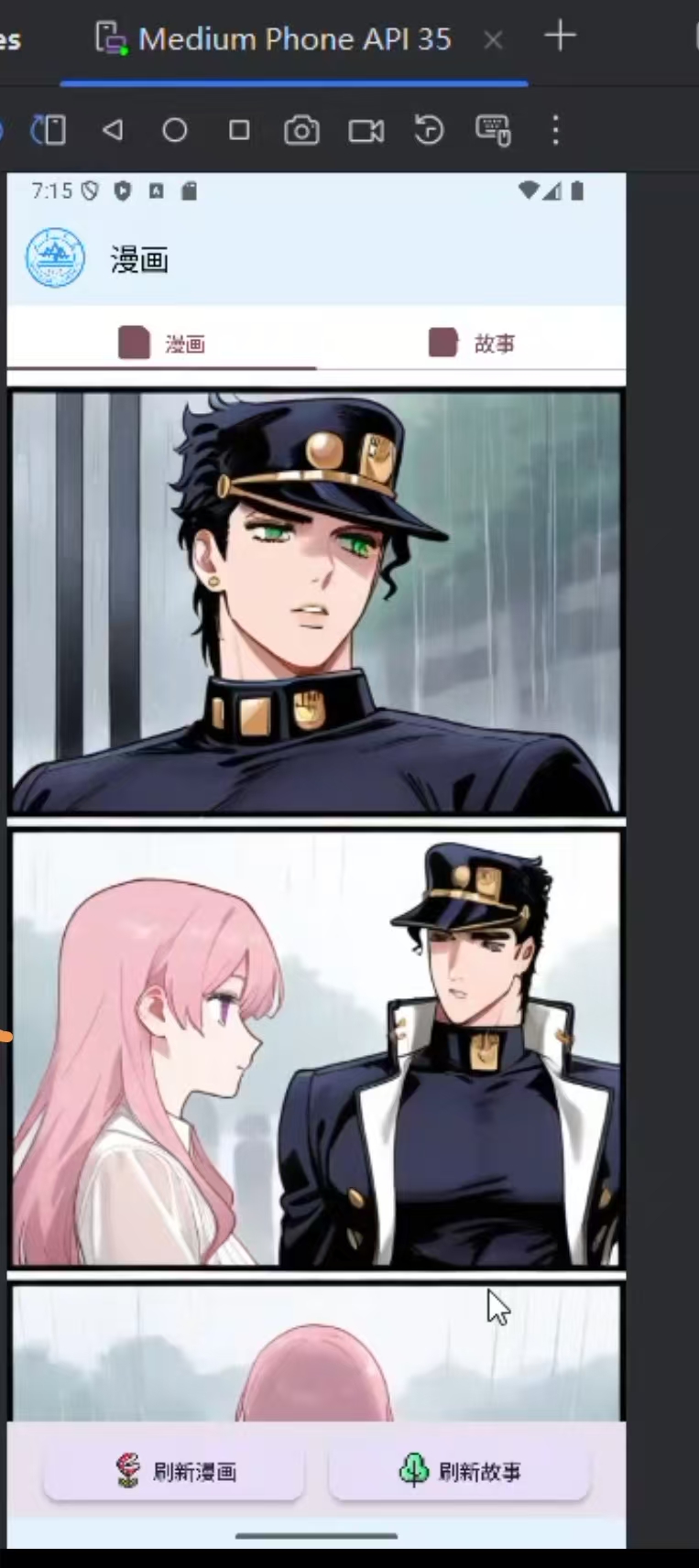


二、四六级真题
1.数据模型类,这个类可以被序列化和反序列化,用于 JSON 格式的转换。data class:Kotlin 的数据类,自动生成 equals(), hashCode(), toString(), copy() 等方法。使用Level 枚举 ,定义了两种级别:CET4 和 CET6 ,均可以序列化。完整代码如下:
@kotlinx.serialization.Serializable
data class Exam(
val title: String,
val level: Level,
val questions: List<Question>
) {
@kotlinx.serialization.Serializable
enum class Level {
CET4, CET6
}
@kotlinx.serialization.Serializable
data class Question(
val id: Int,
val type: QuestionType,
val text: String,
val options: List<String>,
val correctAnswers: List<Int>, // 索引列表,对于单选题只有一个元素,多选题可以有多个
val explanation: String
)
@kotlinx.serialization.Serializable
enum class QuestionType {
SINGLE_CHOICE, MULTIPLE_CHOICE
}
} 2. ExamViewModel文件,管理考试应用的状态和数据
UI 状态管理,使用 mutableStateOf 管理 UI 状态,对外暴露不可变的 State 对象;当前考试集管理,使用 StateFlow 管理当前显示的考试集索引,对外暴露为不可变的 StateFlow。
private val _uiState = mutableStateOf<ExamUiState>(ExamUiState.Loading)
val uiState: State<ExamUiState> = _uiState
private val _currentExamSet = MutableStateFlow(0)
val currentExamSet = _currentExamSet.asStateFlow()在 viewModelScope 协程中执行加载试题,更新当前考试集索引,成功时更新 UI 状态为 Success 并传递对应考试数据,失败时更新 UI 状态为 Error。
fun loadExam(setIndex: Int) {
viewModelScope.launch {
try {
_currentExamSet.value = setIndex
_uiState.value = ExamUiState.Success(_examSets[setIndex])
} catch (e: Exception) {
_uiState.value = ExamUiState.Error(DataResult.Error.Code.UNKNOWN)
}
}
}3.功能界面设计,多组件组合
设计流程图如下:
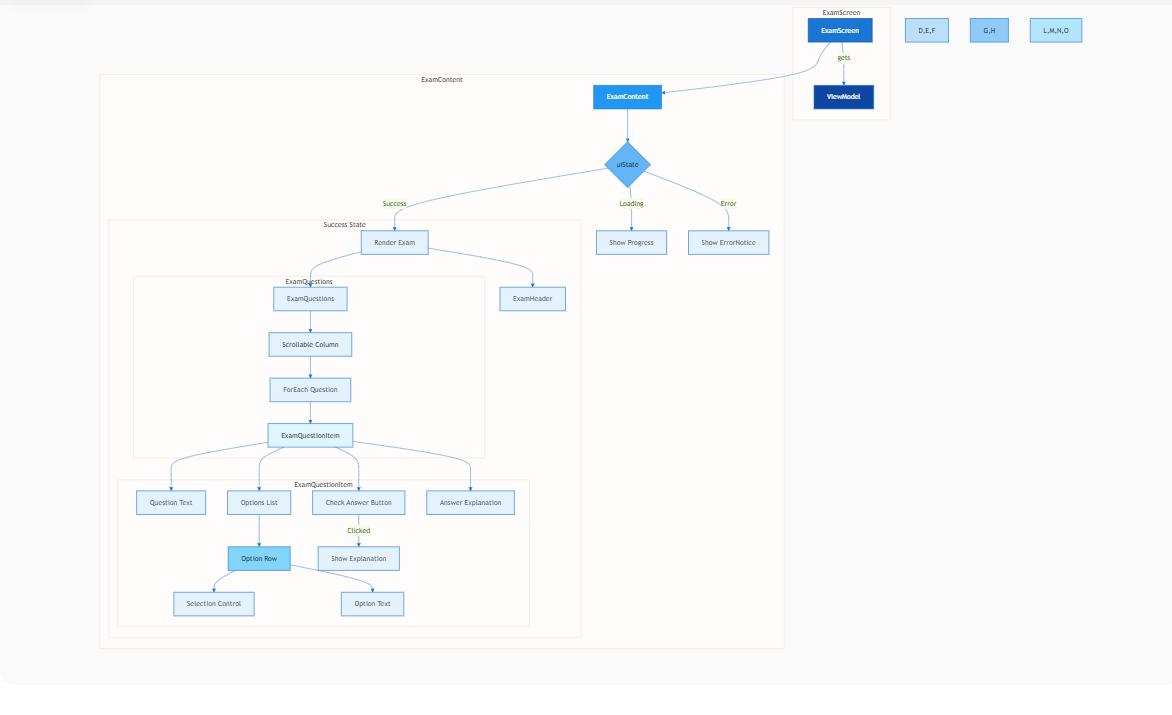
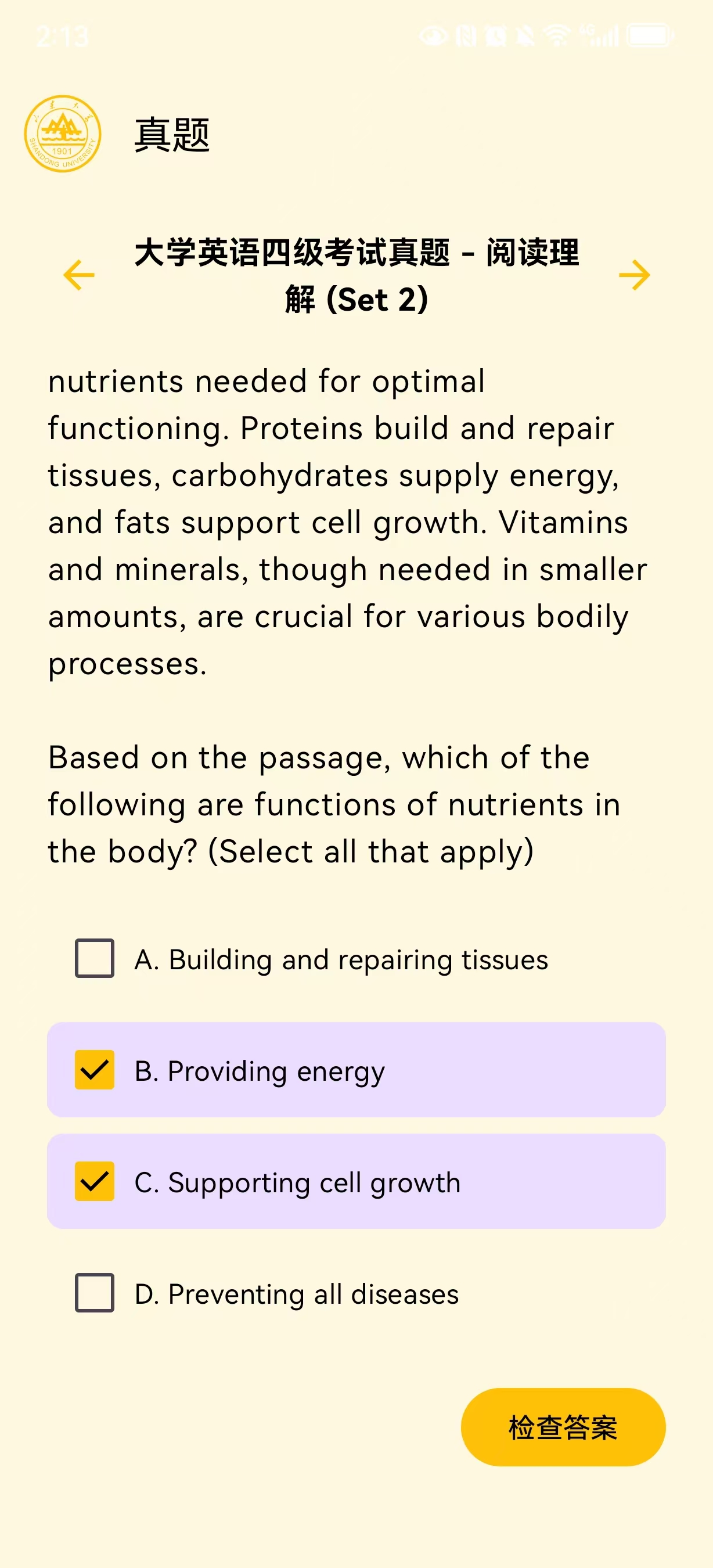
4.实现界面如下:

三、每日阅读功能的开发与实现
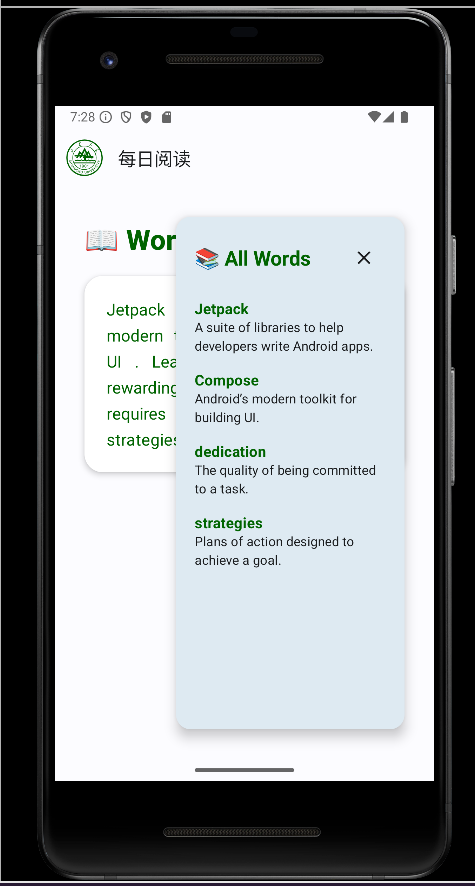
1.功能描述:进行整篇文章的阅读,点击单词显示其释义或翻译,支持侧边栏的显示/隐藏,集成 DeepSeek 翻译服务获取单词翻译,本地缓存已查询过的单词。
2.实现思路:
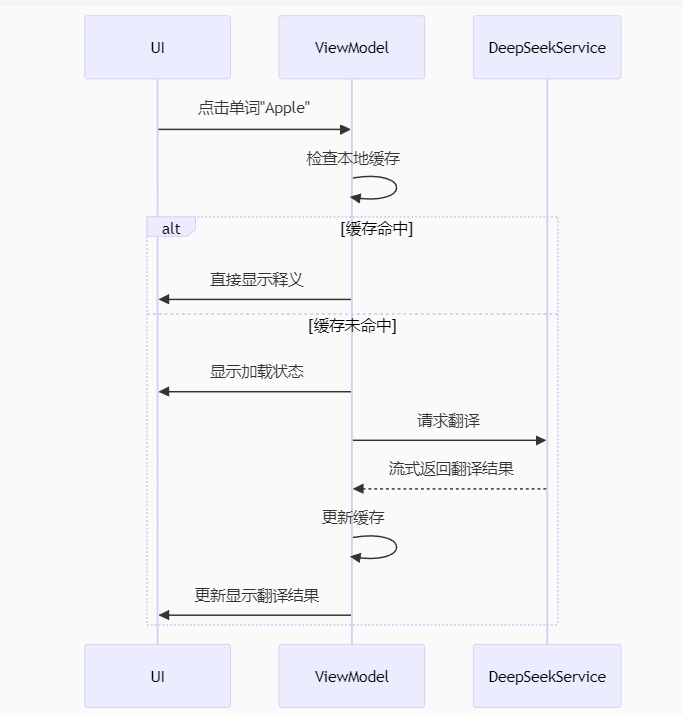
3.实现效果展示:
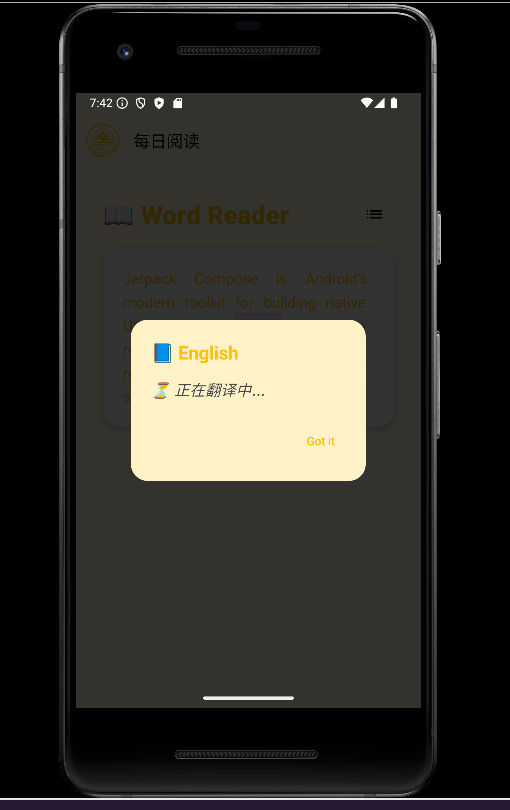
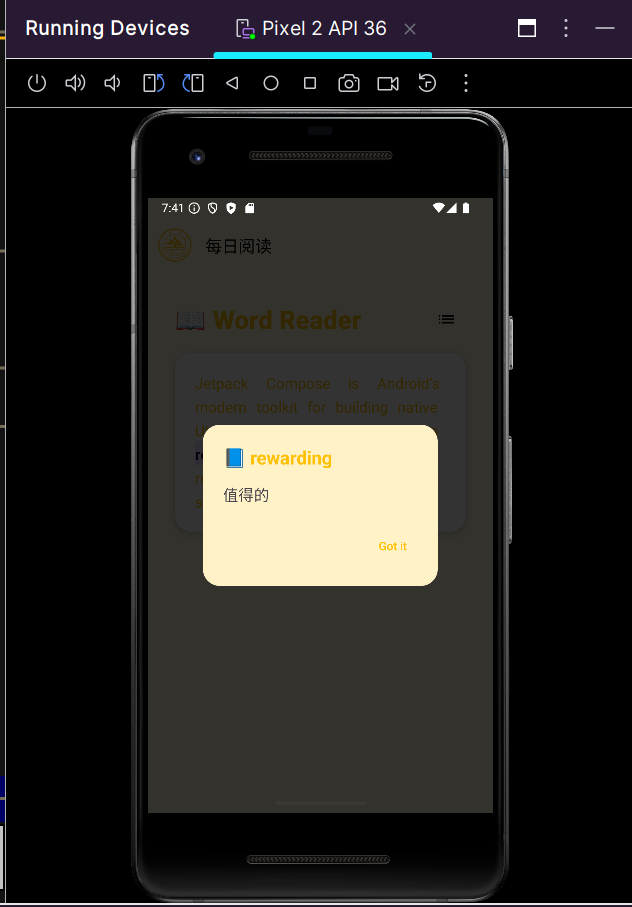
四、部分前端页面的优化
1.帮助界面优化: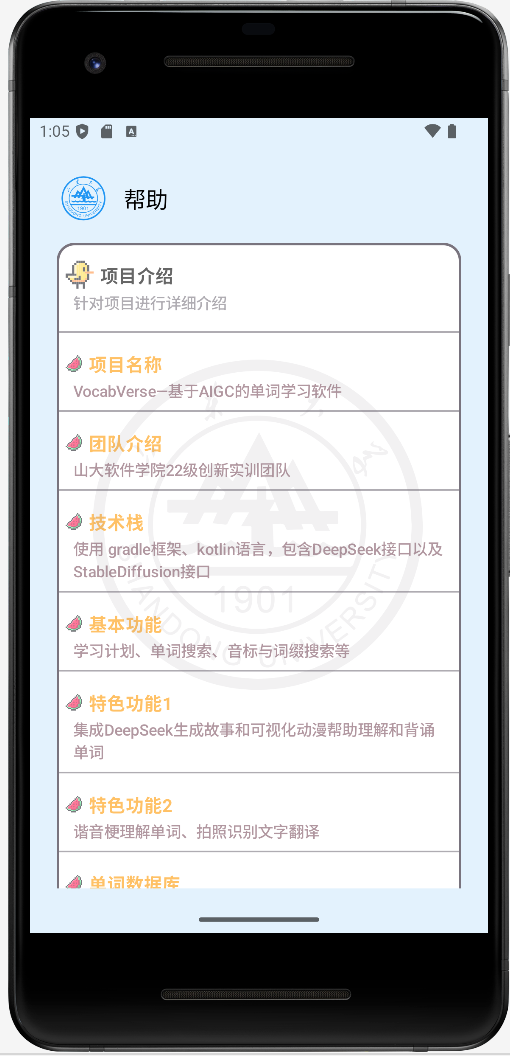
2.默写练习页面优化:

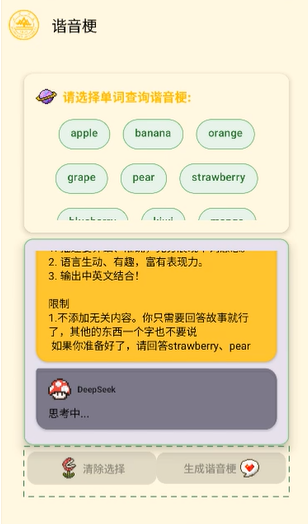
3.谐音梗界面优化:
4.故事界面优化:

更多推荐
 已为社区贡献5条内容
已为社区贡献5条内容









所有评论(0)